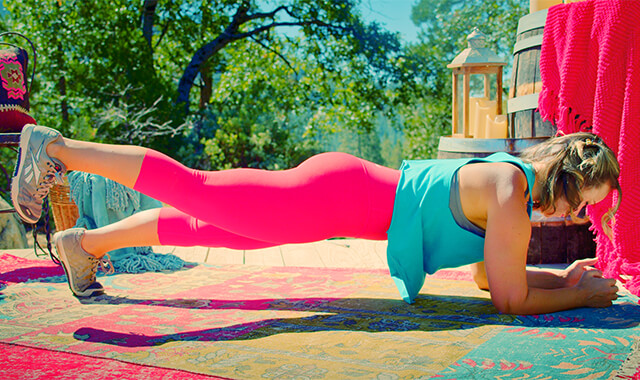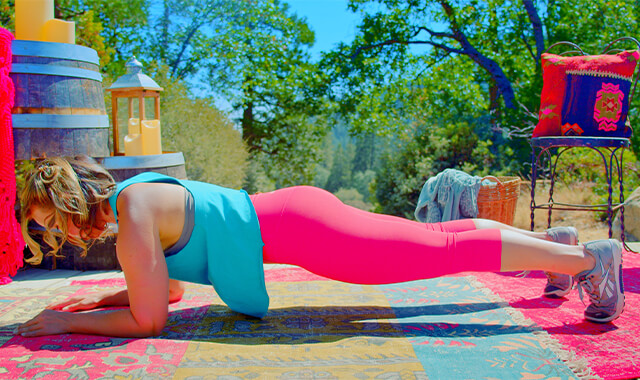dOUBLE Leg Stretch - core Exercise
How to Do the Double Leg Stretch - Pilates Ab Floor Exercise | In-Depth Guide [VISUAL LEARNERS] Advanced
Proper Form, Common Mistakes, Easier & Harder Variations | Home Resistance Training
WHAT DO YOU WANT TO SEE?
QUICK DEMO
QUICK DEMO
MUSCLES THIS WORKS
MUSCLES
MAIN MUSCLES WORKED IN the Double Leg Stretch
TRANSVERSE ABDOMINIS, OBLIQUES, & RECTUS ABDOMINIS
OTHER MUSCLES WORKED:
- Pelvic floor
- Diaphragm
STARTING POINTERS
Starting Pointers
WHAT WE'RE DOING TODAY
ALL WE'RE DOING:
This one is hard to explain with words! Watch the video.
This is an advanced abdominal exercise that challenges the ability of the muscles to work together to stabilize the trunk as the legs are moving. I love it, but it really took me some months to work up to being able to do this. Here's the progression of core exercises you'll want to work through doing capably first as each one gets a bit harder for the muscles:
TA activation exercise (this is essential- without knowing this, you'll do all these exercises wrong)
Now Double Leg Stretch, where you are now.
In the double leg stretch, our abdominals have to work to hold the head and shoulders body slightly lifted from the mat in a stable position. The legs are kept straight and the abdominal muscles have to work hard to hold the weight of the legs up. This is a good exercise for strengthening the transverse abdominis, rectus abdominis, obliques, iliopsoas and rectus femoris.
HOW TO DO THE EXERCISE
LOOKS
HOW Double Leg Stretches SHAPE OUR BODY
Flat stomach, toned and tapered waist, improved posture, confident, graceful movement.
PROPER FORM
PROPER FORM: Double Leg Stretch
EQUIPMENT, SETS & REPS
EQUIPMENT
- Mat
SUGGESTED STARTING WEIGHT FOR WOMEN:
None
SETS & REPS:
8 - 10
PACE:
Controlled movement of arms and legs. Increasing the speed of the movement will increase the muscle activity of the core - maintaining a stable torso.
BODY POSITION
BODY POSITION FOR THE Double Leg Stretch
BODY STANCE: Lie on your back. Knees and hips bent to table top position - thighs perpendicular to the floor and shins parallel to the floor. [It is helpful to position one leg and then the other leg so that you are able to keep the spine neutral and the abdominals engaged].
ARMS: Gently holding the back of your thighs (close to the knee).
NECK: Curl your head up, with your chin moving down towards your chest.
UPPER BACK: Continue to curl your thoracic spine up so that your shoulders are off of the floor, you should feel like you are pivoting around the end of your sternum.
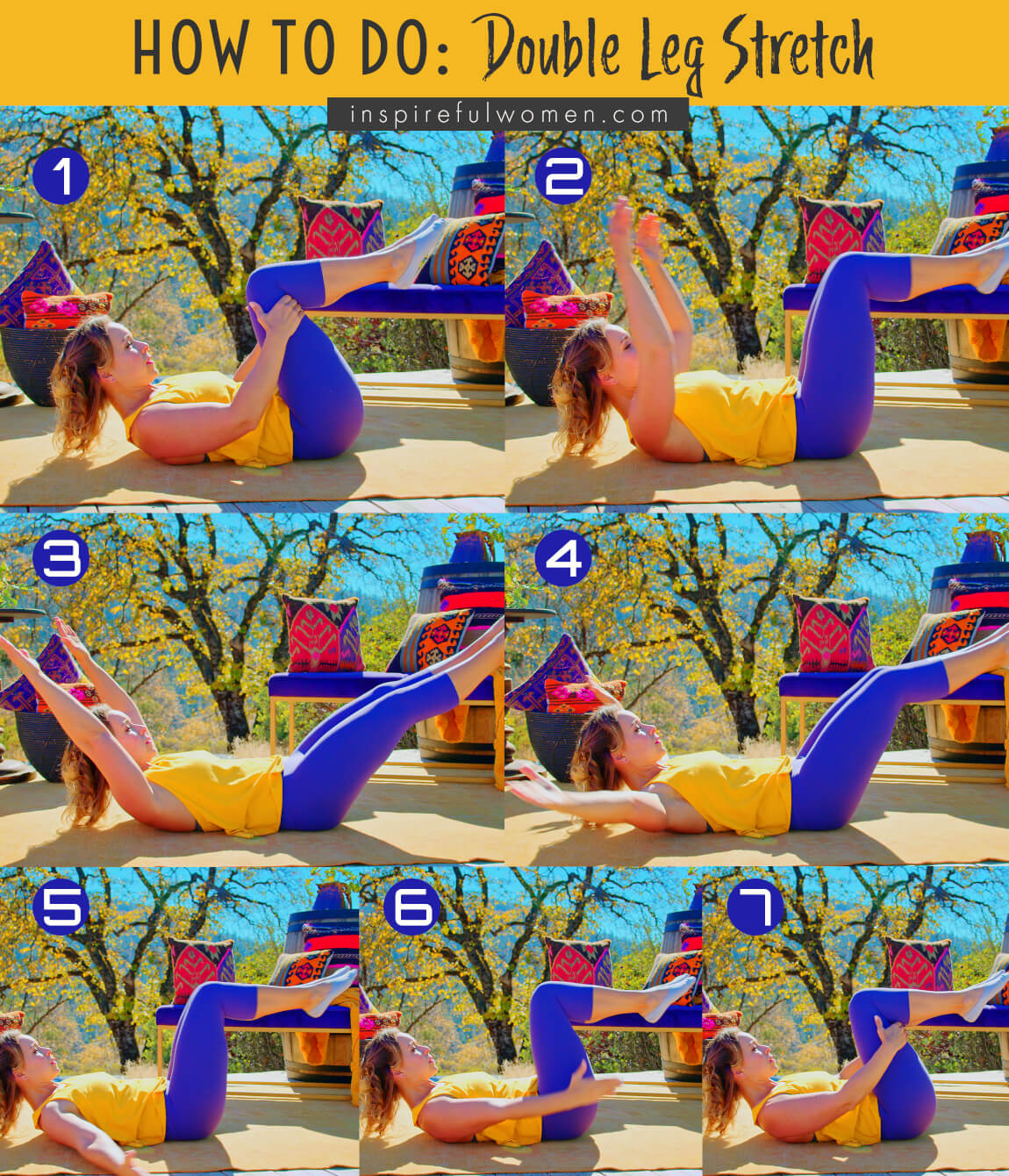
HOW TO DO
HOW TO DO Double Leg Stretches
CUE: Your head, neck and shoulders should feel like they are stacked over your thoracic spine. The effort should be in your abdominal muscles not your neck and upper back.
Extend both legs and both arms out - energized down to your fingers and toes. Your arms are stretched overhead, with your upper arm by your ears in the end position. Your hips bent about halfway between being straight out on the floor and all the way up with your foot parallel to the ceiling (45 degrees). Pause in this position.
Circle your arms down (around to the sides of the torso) your hands reaching for your lower legs. Your hips and knees will bend a little more than 90 degrees. Your arms move straight overhead when your legs stretch out, and then circle down and around (snow angel motion) as your knees pull back in.
Repeat for your designed number of reps.
The movement of your legs and arms should be smooth and controlled with the focus on keeping your torso still.
HOW TO SAFELY GET OUT OF THE EXERCISE
Bring your hands down. Lower one leg to the floor, lower the other leg to the floor. Roll to your side and sit up.

COMMON MISTAKES
COMMON MISTAKES
WHAT TO AVOID WITH THE Double Leg Stretch
KEY TIP:
Guess what? Good news! Many avoids are the same for most movements. Once you learn the basics, there's really only a few extra avoids for each individual movement.
1. Avoid Abs Bulging Out
AVOID: Avoid letting your abdominal muscles bulge out.
WHY NOT?
- This is the most common mistake.
- You should not see your lower abdomen pooch or bulge out when the abdominal muscles are active.
- This means that you are pushing your rectus abdominis (6-pack muscle) out instead of using your transverse abdominis to stabilize your midsection.
WHAT TO DO:
- This most frequently happens when you are first lifting the legs or when your core muscles get tired.
- Make sure to lift one leg at a time, concentrating on pulling the belly down towards the spine without flattening your low back.
- Correct activation of your abdominal muscles will result in a flat or slightly “scooped” out appearance of your lower abdominals.
- If you are unable to activate your abdominals without them bulging out
- Work on pulling your belly button down towards your spine in a hook lying position (feet on the floor, knees bent)
- Add in controlled breathing while maintaining the position.
- Master this exercise before progressing core exercises.

2. Avoid Arching Low Back
AVOID: Avoid arching your low back.
WHAT TO DO:
- Maintain a neutral spine position to prevent low back joint injury, muscle strain or damage over time.
- If your ribs lower ribs flare upwards or your belly is lifted up - this indicates you are arching your low back. Your pubic bone and front hip bones should be in one plane - can check by placing fingertips on the pubic bone and set the base of your palm on the hip bones - your hand should be flat.
- This can happen if you move the arms up too far overhead or your legs too close to the floor.
- Limit how far you move your limbs.

3. Avoid Flattening Low Back
AVOID: Avoid flattening your low back.
WHAT TO DO:
- Maintain a neutral spine position to prevent injury or muscle strain.
- You should not be able to feel your low back pressed into the floor.
- Work on activating your core muscles without flattening your low back.

4. Avoid Holding your Breath
AVOID: Avoid holding your breath.
WHAT TO DO:
- When first learning core exercises it can be difficult to keep the abdominals activated and continue a normal breathing pattern.
- Inhaling and exhaling will increase the core muscle activity, and bring oxygen to the muscles as they work.
- It is helpful to work on abdominal muscle activation coordinated with breathing before adding the leg movement.

MAKE IT HARDER
HARDER
MAKING THE Double LEG STRETCH MORE CHALLENGING
Small Pulse
Small Pulse
With the legs and arms stretched out, lower them both a few inches, lift back up and complete the rep. The abdominal muscles will need to work harder the closer the legs and arms are to parallel with the floor.

MAKE IT EASIER
EASIER
MAKE THE Double Leg Stretch MORE DOABLE
Leave Head On Floor
Keep Head On Ground
If you have any neck pain or history of neck injury, leave your head on the floor (neck supported with a washcloth , if needed). This is a good option for learning the form, or for weaker abdominals.

LEGS AND ARMS CLOSER TO THE MIDSECTION
Arms & Legs More Vertical
Instead of reaching the legs and arms out away from the midsection, move them up so the arms and legs will be closer to perpendicular to the ceiling - the hands closer to the shoulders and the feet closer to the ceiling. This will be easier on the abdominal muscles.

WHAT WE'RE DOING TODAY
WHAT & WHY
BENEFITS OF TRAINING THE core muscles
WHAT
LAYING DOWN EXERCISES YAY
This is one of my favorite core exercises. I will probably end up writing this on every core exercise blogpost, but core exercises have changed the strength of my body a LOT. I am able to have a good comparison because, welp, embarrassingly I never did them before at all. I didn't really understand their value so I skipped them. I feel so different in my body when exercising and doing daily life now that these movements have been a part of my regular workout routine.
These movements are done lying down on your back, making them a nice way to start or end your day. Lying down lets you concentrate on activating the abdominal muscles without worrying about the back muscles. These exercises seem pretty simple but they can be very challenging and do a great job of activating the core.
MAIN MUSCLE WE ARE TRYING TO ACTIVATE
It is important to really understand and feel the abdominal muscles working the way they are supposed to work. The main muscle you are trying to activate is the transverse abdominis which is deep - deeper than the rectus abdominis (6-pack) muscle. This is the corset muscle - it is attached to the ribs, the pelvis, iliopsoas, and connective tissue in the front of the torso, and wraps around your midsection to join the fascia that attaches to the back muscles. When activated it feels like you have shrink-wrapped your mid-section, just like cinching up a corset or back brace. If you have never heard of this muscle before and have no idea how to activate it, start with the Transverse Abdominis Activation exercise before moving on to the others.
The key to the core exercises is being able to find and activate this muscle. The transverse abdominis muscle runs across your midsection, from the ribs to the public bone, around the sides of the torso, and attaches to the spine through fascia, it is like a big back brace. It is one of the most important spinal stabilizers, unfortunately, many people are not even aware of it and they don’t know how to activate it. A bonus is to be able to activate the pelvic floor muscles at the same time. This will take time and concentration. The biggest mistake people make is that they are not patient enough to make sure they are using the correct muscles and they progress the exercises too quickly. This set of exercises is designed for making it easy to feel the correct muscles working.
WHY BOTHER DOING IT?
WHY
WHY DO WE EVEN CARE?
Core exercises should be considered the foundation for all exercises - you must be able to stabilize your midsection to be able to use your arms and legs in a healthy and effective way.
TYPE OF CORE EXERCISES MATTER
Exercises like sit ups, crunches or Russian twists, involve holding the legs and arms still and moving the low back (lumbar spine) over and over again. Sometimes this is even done while holding weight. This type of movement trains the muscles to move through the spine. This type of exercise, bending over & over at the spine, will actually weaken the tissues that support the spine, the ligaments and discs. These exercises work the rectus abdominis muscle which acts to bend the back (flex), it does not stabilize the spine, it does not even attach to the spine.
Exercises that train our core muscles to stabilize the spine instead of moving the spine helps to prevent damage to the low back. This is what most physical therapists will tell you.
HELPS HAVE THE STRENGTH, BALANCE & COORDINATION NEEDED TO DO EVERYTHING BETTER & MORE EFFICIENTLY
Unfortunately, a very high number of people in the U.S. will have back pain at some point in their lives. Also, once you start lifting weights to increase the strength of your legs and arms, or increase your activity to include heavy work like shoveling, you want to be sure that your core muscles are strong enough to keep up.
Strong and healthy abdominals impact just about everything we do in our daily lives. When the abs are stronger you can move with less effort, lift more, carry more, and walk and bike further. The core muscles are the center of the body - they all work together to coordinate the lower and upper body and the left and right sides of the body. Healthy core muscles will improve balance and coordination.
Learning how to move and exercise with good form will help prevent back pain, and if you injure your back, having good core strength will help you recover more quickly. Core exercises will increase the strength of your core, but more importantly, the exercises train the muscle how to do their job. Their job is to make subtle coordinated changes constantly in order to hold and move the body. These exercises train the muscles of the torso for endurance, strength, and motor control (the ability of the muscles to work together to stabilize the trunk as the arms and legs are moving). Many people are unsure of how to activate their core muscles, especially the transverse abdominis. The main job of the transverse abdominis is to compress and stabilize the midsection. The core muscles need to work together all day long, in a highly coordinated fashion to keep us upright during all of our daily activities.
If you have ever had back pain or an injury, complex pregnancies and/or deliveries, pelvic floor pain, abdominal surgery, including cesarean sections - sometimes the transverse abdominis is not responsive. It is not uncommon for muscles to “shut down” after pain or injury. And in the case of abdominal surgeries, it is necessary to get through these muscles. Different surgeons have different approaches, but to get through to the contents of the abdomen, you must get through the muscles, so the muscles have been injured. After the surgery or trauma, the muscles need to be re-educated, to learn to do their job. This is no different than rehabilitation after a sprain, strain, or tear of the other muscles in your body.
Untrained core muscles don’t always cause back or neck pain, when the core is not stable, it affects the way we use our arms and legs. Poorly trained core muscles can cause hip, knee, ankle, foot, shoulder, and arm pain or injury.
These exercises focus on activating the muscles that compress the abdomen. The muscles support and protect the internal organs, including the liver, stomach, intestines, and bladder. Increasing the intra abdominal pressure by activating the muscles improves the function of the internal organs including digestion, bladder and bowel control, and breathing.
EVERYDAY LIFE
EVERYDAY LIFE &
MUSCLE FUNCTION
HOW WE USE OUR Core MUSCLES IN EVERYDAY LIFE
1. THE TRANSVERSE ABDOMINIS, AND OBLIQUES WORK ALL DAY LONG TO STABILIZE THE SPINE DURING DAILY ACTIVITIES:
- Walking
- Running
- Dancing
- Lifting
- Pulling
- Carrying
- Pushing a wheelbarrow
- Washing windows
- Kicking or throwing a ball
- Reaching
- Climbing stairs/ladder
- Stepping into a high car/truck
- Golf
- Painting overhead
- Vacuuming
- Sweeping
- Gardening
2. THE RECTUS ABDOMINIS FLEXES THE SPINE
- Sitting up from lying down - like getting out of bed
- Prevents you from falling backward - balancing on a ladder while washing windows or painting.
3. THE TRANSVERSE ABDOMINIS, OBLIQUES, DIAPHRAGM, AND PELVIC FLOOR COMPRESS THE ABDOMEN
- Going to the bathroom
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Laughing
- Supports the internal organs for improved function - especially digestion
HOW TO FEEL WHAT MUSCLE IS WORKING
How to Feel What Muscle is Working
The most important muscle to activate for this group of exercises is the transverse abdominis muscle. This is a hard muscle to find. It is broad and deep. When you activate this muscle the belly button and spine move closer together, the ribs on the left and right sides of the front of the torso come in closer together. You should feel like you are tightening up a corset or shrink-wrapping your midsection.
Transverse abdominis: Lie on your back, knees bent. Find the two pointy parts on the front of your pelvis. Drop your fingers down off of the bony part, in the direction of your belly button. Now clear your throat. You should feel the transverse abdominis contract under your fingertips.
If you cannot find this muscle, or if you are unsure if you are doing it right, try the Transverse Abdominis Activation exercise.
SCIENCY STUFF
SCIENCY STUFF
SPIFFILICIOUS FACTS ABOUT MUSCLES & MOVES
It could be argued that it is not necessary to do specific exercises for your core muscles because you are using them all day long. This is true to some extent. If you are relatively active, with good posture, good control over your midsection, you have established healthy movement patterns - keeping your spine neutral and stable during heavy lifting or repetitive movement, and have no history of back pain, or abdominal surgery (cesarean sections, hysterectomies) or complications/difficulty in pregnancy or childbirth, then you may not have to do specific core exercises - because you are using those muscles correctly all day long.
ALLLL MUSCLES & WHEN
ALL MUSCLES WORKING & WHEN DURING THE Double Leg Stretch
All of the muscles of the torso will be working to stabilize throughout the movement.
The rectus abdominis works hard to stabilize the trunk in the beginning position - with the head and shoulders lifted up off of the floor.
The quadriceps works concentrically to straighten the knees, while the rectus femoris and iliopsoas work eccentrically to control the downward force of gravity as the legs reach out. The anterior deltoid and biceps move the shoulder into flexion and the lats and triceps will control the movement once the arms move past being straight up over the chest, the force of gravity begins to pull them downwards.
The abdominal muscles will work harder when the legs and arms are outstretched.
The iliopsoas and rectus femoris contract concentrically to pull the thighs back into the tabletop position. The latissimus dorsi works concentrically to pull the arms down to the sides.
PIN IT FOR LATER!