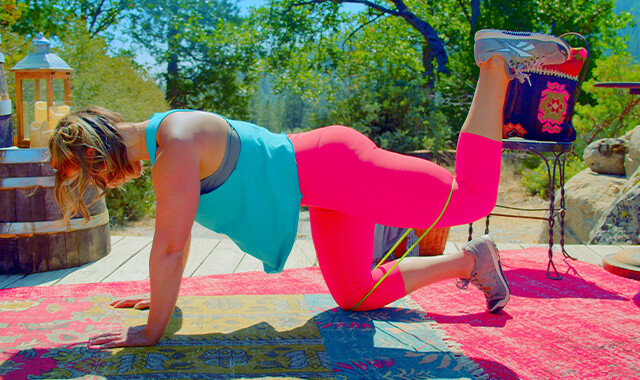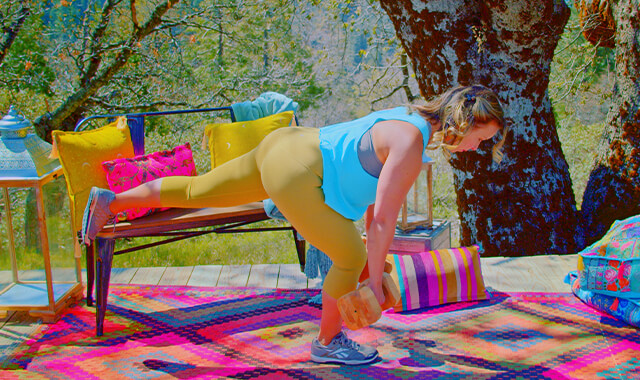Donkey Kicks - Bent Leg
How to Do Bodyweight Donkey Kicks - Easy Glute Activation Exercise | In-Depth Guide [VISUAL LEARNERS] Beginner
Proper Form, Common Mistakes, Variations + Easier | Home Resistance Training
WHAT DO YOU WANT TO SEE?
QUICK DEMO
QUICK DEMO
MUSCLES THIS WORKS
MUSCLES
MAIN MUSCLES WORKED IN the Donkey Kick
Gluteus maximus
OTHER MUSCLES WORKED:
- Hamstrings
- Adductor Magnus
- Gluteus Medius and Minimis
WHAT WE'RE DOING TODAY
WHAT & WHY
BENEFITS OF TRAINING THE Gluteus maximus
WHAT
WHAT WE'RE DOING TODAY
Other names for this exercise: Bent Knee Glute Kickbacks. 4 Point Bent Knee Hip Extensions
ALL WE'RE DOING:
On all fours, lift your thigh up into the air. Done!
GET ALL THE GLUTES GOIN' ON
Donkey Kicks target the gluteus maximus muscle which is the largest muscle of the buttocks. The exercise is done on all 4s - hands and knees position. One leg is lifted with a bent knee, and the thigh is lifted up into hip extension. This will target the hip extensors, with a focus on the gluteus maximus. The exercise also works the smaller gluteus medius and minimus on the “non-working” side. When you are supported by only one leg, the muscles on the side of the hip, the gluteus medius and minimus, are responsible for holding the pelvis in the right position. The position works the arms and the leg that are stabilizing the body on the floor during the movement of the other leg.
TRICKY TO GET RIGHT BUT WORTHWILE EXERCISE
This exercise is frequently done with poor form. Many people let their backs move - rounding and arching the back, instead of moving the thigh in the hip socket. The hip joint is made up of the socket which is the lower part of the pelvis and the ball of the thigh bone (femur). The focus should be on keeping the pelvis very still while isolating the movement, moving only the thigh in the hip joint. The gluteus maximus works to pull the thigh back in the hip joint (hip extension). If the pelvis moves then this is no longer hip extension - it is low back extension. The core muscles need to be active to prevent your back and pelvis from moving. In the Donkey Kick, the knee is held in a bent position (90 degrees) the hamstring will be holding the knee bent, this will encourage the gluteus maximus to do more of the work to lift the thigh back.
BEGINNER RESISTANCE FOR NEWBIES TO GLUTE TRAINING
Many of the glute targeting exercises are done lying on your back and using the glutes to lift the pelvis up. For example bridges and hip thrusts. This requires you to be able to lift much of the weight of your body up against gravity. This may be easy when you are using both of your legs, but when you progress to a single leg, it can be quite challenging. Donkey Kicks are done in the hands and knees position, using one leg at a time, and you are just lifting the weight of the leg up against gravity. When the knee is bent the stress on the hip muscles is even less. When you are trying to activate and isolate one muscle group, it is nice to be able to limit how much weight you are lifting to make sure you are using the right muscles. If you are forced to lift a set amount of weight (as in the other exercises), if you are not strong enough, other muscles will have to kick in to help. Glute Kickbacks in the hands and knees position is really good for trying to isolate and learn to activate one gluteus maximus muscle at a time.
WHY BOTHER DOING IT?
WHY
WHY DO WE EVEN CARE?
Strong glutes help keep the spine, pelvis, hips, and knees healthy. They work with all of the other muscles of the core and legs to keep the joints aligned and cushion the impact during walking, running, and jumping. Strong glutes and leg muscles can be used to do most of the work when lifting and moving heavy objects. This will decrease the stress on the spine and help to prevent damage and degenerative changes that occur with age.
Surprisingly, many people have a hard time activating their gluteus maximus muscle. And, even when they are able to activate their gluteus maximus, they have trouble activating only one side at a time, they both want to contract at the same time. The problem with this is that when we walk, run, and climb stairs, one gluteus maximus is working and the other is not. Training the gluteus maximus to work, and work independently is important for protecting the spine and lower body from injuries. If the gluteus maximus is not working correctly, the body will compensate and use other ways of accomplishing the end goal. A perfect example of this is glute kickbacks. Probably the most common error in this exercise is not using the gluteus maximus to lift the leg. Instead, the low back collapses, sagging at the midsection. When this happens, you can lift the leg higher with less muscle activity. The foot gets higher but the hip is not going into as much extension. The gluteus maximus is most active towards the end range of extension. If the hip never gets past neutral, the hamstrings will be able to do more of the work. Not only is this bad mechanics because the spine is moving through a rounded position and an arched position, it will also use the muscles of the back and the hamstrings without much involvement from the gluteus maximus. Over time, the gluteus maximus will get weaker. the range of motion of the hip joint into extension will get tighter, and the spine will become more mobile - exactly the opposite of what you want. Ideally, the spine is stable, and the movement and power come from the joints and muscles of the legs.
Tight hip flexors can interfere with the gluteus maximus’ ability to contract. Muscles that are on opposite sides of a joint, and do opposite actions, work in pairs. When one muscle is working to move the limb, the other one is quiet, it basically “turns off”. This is so that the muscles are not competing, and working against each other. For example, when the hip flexors are trying to pull the thigh forward, the gluteus maximus will not be able to hold the leg back and prevent the hip flexor from doing its job.
Anytime that you exercise in the hands and knees position while lifting one leg or one arm off of the floor, the core muscles work differently. When one leg is lifted from the floor, the pelvis on that side is unsupported and gravity will pull down on it. The obliques and quadratus lumborum - two of the core muscles that work to prevent rotation and side-bending of the trunk, will need to work harder to keep the spine in a neutral position. It is a good idea to include exercises that work these muscles as you are moving the legs because that is how we use our bodies in everyday life. Examples of this in everyday life would be standing on a ladder, lifting one leg to reach further - I was doing this the other day picking peaches. The core muscles have to really kick in to help maintain your balance and prevent you from falling from the ladder.
EVERYDAY LIFE
EVERYDAY LIFE &
MUSCLE FUNCTION
HOW WE USE OUR Gluteus maximus IN EVERYDAY LIFE
1. THE GLUTEUS MAXIMUS MOVES THE THIGH BACK FROM A BENT POSITION TO STRAIGHTEN THE HIP (HIP EXTENSION)
- Transitioning from sitting to stand
- Standing upright with good posture
- Running and walking uphill
- Jumping
- Standing back up from squatting down
- Lifting items from the floor
2. HELP TO TRANSFER POWER FROM THE LEGS TO THE ARMS
- Batting
- Golfing
- Tennis
- Shoveling
- Vacuuming
- Throwing a ball
3. STRAIGHTENING (EXTENSION) THE HIP
- Walking
- Running
- Moving from sitting to standing
- From a chair
- Out of a car
- Off of the toilet
- Going up and down stairs
- Getting up from squatting
- Lifting from the floor
- Getting up from the floor
- Standing up from a bent-over position
- Unloading a dishwasher/dryer
4. HOLDS THE BODY UPRIGHT
- Standing
5. RESTRAINING/BREAKING THE PULL OF GRAVITY ON THE UPPER BODY
- Leaning over - prevents the torso from being pulled down
STARTING POINTERS
Starting Pointers
This version of glute kickbacks is done with the knee bent to about 90 degrees (right angle). Bending the knee puts the hamstrings in a shortened position so that they will not help as much when you lift the thigh back. The gluteus maximus will be working to lift the weight of the leg. This position also makes it pretty easy to lift the thigh past the torso - behind the body. This is a great version of the glute kickbacks to use for people who have difficulty using one glute independently - waking up the muscle and getting it to do its share of the work. It is important to make sure that the abdominal muscles are working to prevent the low back from moving.
Bending the knee will decrease the load on the gluteus maximus a little bit - because the distance between the hip joint and the leg is shortened - instead of lifting the leg stretched out from hip to foot, the distance is only from the hip to the knee. This movement is really good for trying to isolate the gluteus maximus muscle and feel how it works to lift the leg back behind the torso, into hip extension. In order to advance the exercise and work on increasing the strength of the gluteus maximus, you can progress to the dumbbell or banded versions of the movement.
HOW TO FEEL WHAT MUSCLE IS WORKING
How to Feel What Muscle is Working
Stand facing away from a wall. Bend your knee and place the bottom of one foot on the wall. Place your hands on your buttocks - one on each side. With the leg that is on the wall - push back into the wall. You should feel that side of the buttocks tighten up, while the other stays relaxed. If you are unable to contract one side while keeping the other relaxed, work on this before progressing to the glute kickbacks.
HOW TO DO THE EXERCISE
LOOKS
HOW Donkey Kicks - Bent Leg SHAPE OUR BODY
Firm and lifted buttocks.
PROPER FORM
PROPER FORM: Donkey Kicks - Bent Leg
EQUIPMENT, SETS & REPS
EQUIPMENT
Mat
SUGGESTED STARTING WEIGHT FOR WOMEN:
None
SETS & REPS:
2 sets of 8 reps on each side.
PACE:
Moderate.
BODY POSITION
BODY POSITION FOR THE Donkey Kicks - Bent Leg
BODY POSITION: Hands and knees. Neutral spine and pelvis, abdominals activated. Neck lengthened, eyes down. Sternum lifted, chest open, shoulder blades together and down your back. Position your knees directly under your hips with your thighs straight up and down (vertical, perpendicular to the floor). Hips are bent to 90 degrees, knees are bent to 90 degrees. If you have one thigh longer than the other (if you cannot get the back of your pelvis level when both knees are straight below your hips), it is fine to start with your knee of your working leg pushed back - so it will not be directly under your hip, your hip of your working leg will be less bent.
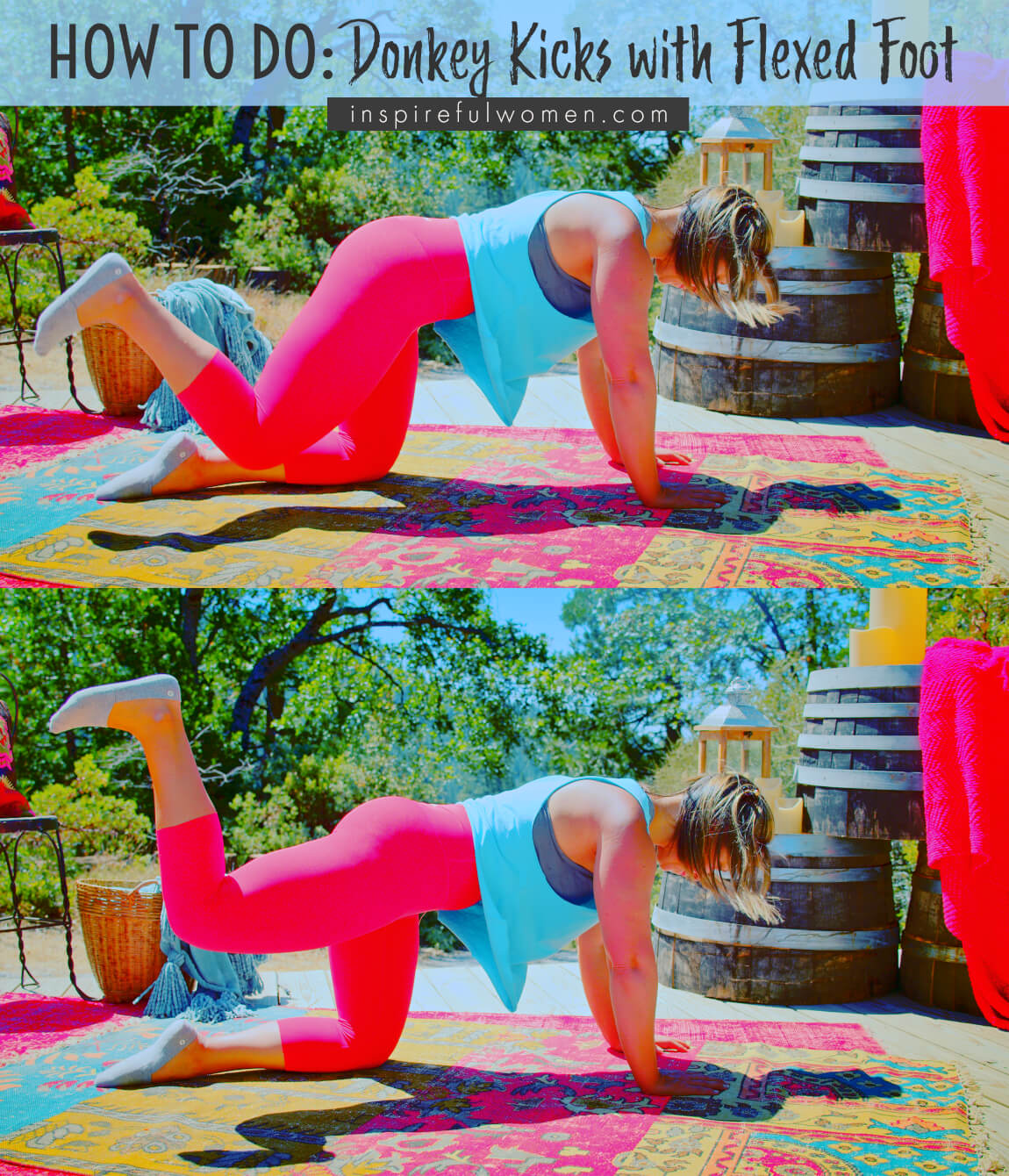
FEET: The top of your foot can be resting on the floor, toes pointing back or your ankle can be bent with your toes on the floor. The foot of your working leg should be flexed or pointed, whatever is most comfortable.
ARMS: Directly under shoulders, hands flat, fingers pointed forward. Arms near straight - can have a slight bend at your elbows if that is more comfortable- avoid locking your elbows. If this position hurts your wrists you can do this with hands fisted.
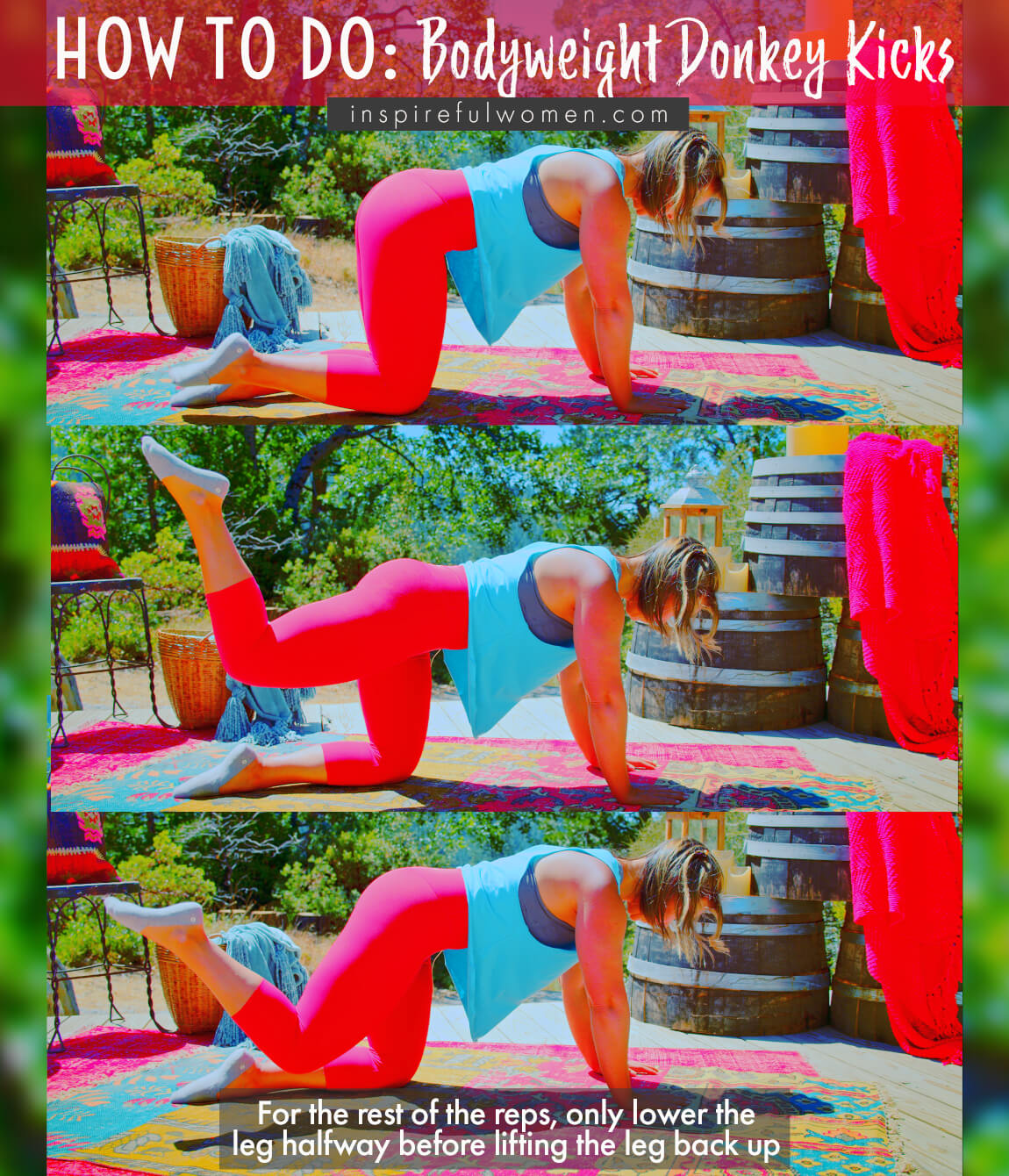
HOW TO DO
HOW TO DO Donkey Kick - bent leg
CUE: Focus on using your gluteus maximus to lift your thigh up (back behind the body). There should not be any movement in your back or your pelvis.
Without leaning towards your other knee (supporting leg), slide your working leg back. As you take the weight off of your working leg, your arm on that side will need to support more of your weight. Keep your knee bent to 90 degrees.
Keep your back and pelvis level - no tipping to the side opposite of your lifting leg. You should be able to lie a pole across your back and it would be level.
Lift your thigh as far as you can without moving your pelvis. Hold for 2-3 seconds, focusing on squeezing your gluteus maximus.
Lower your thigh down halfway and then lift it back up for the next rep.
HOW TO SAFELY GET OUT OF THE EXERCISE
Lower your knee back down to the floor, push back into kneeling, bring one leg forward, and push up to standing.


COMMON MISTAKES
COMMON MISTAKES
WHAT TO AVOID WITH THE Donkey Kick - Bent leg
KEY TIP:
Guess what? Good news! Many avoids are the same for most movements. Once you learn the basics, there's really only a few extra avoids for each individual movement.
1. Avoid Lifting Leg Too High
AVOID: Avoid lifting the leg too high.
- This is the most common error.
- This movement is coming from the back instead of the hip, basically, the back is just collapsing and gravity is pulling it into an arch.
WHY NOT?
- This can irritate the small joints of the spine.
- This will decrease the muscle activity of the gluteus maximus and the core muscles.
- There is no benefit to lifting the leg higher, it decreases the muscle activity of the leg.

2. Avoid Weight Shifting to Nonworking Side
AVOID: Avoid leaning your body towards the “non-working” side.
WHY NOT?
- This will change the muscle activity of the working leg
- When the torso leans away from the side of the “non-working” leg one of two things can happen
- The hip is now lifting to the side - working the muscles that lift the leg out to the side.
- If the leg is still lifting straight back, it is no longer lifting directly against gravity - it is lifting at an angle so the load on the muscles will be less.
- Decreases the work of the back extensors.
- The arm on the side of the working leg will need to support more weight when the leg is lifted from the floor.

3. Avoid Bending Spine Arching Sagging
AVOID: Avoid moving the back or pelvis as you lift and lower the leg.
WHY NOT?
- This is a common error - mistaking back movement for leg movement.
- This can lead to irritation of the small joints of the pelvis and spine.
- This will decrease the muscle activity of the hip extensors.
WHAT TO DO:
- The goal of the exercise is to isolate the movement to the hip joint -moving the thigh bone forward and backward in the hip socket.

4. Avoid Bending Knee Too Much
AVOID: Avoid letting the working knee bend more than 90 degrees.
WHY NOT?
- Bending the knee more than 90 degrees (a right angle) will lessen the load on the muscles.
- The further the foot is away from the hip the harder the muscles will need to work.
WHAT TO DO:
- Think of pushing the sole of the foot straight up to the ceiling.

5. Avoid Shifting Weight Forward To Torso Arms
AVOID: Avoid shifting your weight forward to your upper body when the leg lifts up.
WHY NOT?
- This will give you the illusion of lifting the leg up higher, but you really are dropping the upper body down instead of lifting the leg.
- Frequently this happens when you bend your elbows every time you lift your leg, leaning your weight onto your arms.

6. Avoid Knee Moving Outward
AVOID: Avoid letting the thigh of the lifted leg travel out to the side when you rotate the leg.
WHY NOT?
- This will reduce the muscle activity of the gluteus maximus.
WHAT TO DO:
- Keep the knee right in line with the hip and shoulder during the lift and the rotation.

VARIATIONS
VARIATIONS
VARIATIONS OF Donkey Kicks - bent leg
Donkey kicks with fists
Neutral Wrist Options: With Fists

Fists + foam pad under knees
Neutral Wrist Options: With Fists + Foam Pad Under Knees

Donkey kicks with Pushup handles + Foam Pad
Neutral Wrist Options: With Pushup Handles + Foam Pad

MAKE IT EASIER
EASIER
MAKE THE Donkey Kick - bent leg MORE DOABLE
On Forearms
Donkey Kicks On Forearms & knees
This is a good option if you experience discomfort in your wrists or elbows in the hands and knees position. From the hands and knees position, bend the elbows and place the forearms on the floor. The hands can come into midline to form a triangle between the two elbows and the hands if that is more comfortable, or they can be straight out in front. The elbows should be right under the shoulders.
This position will decrease the muscle activity of the forearm muscles and the scapular and shoulder muscles will be less active - because the position is more stable, they will not have to work as hard.

Knee to Ground Each Rep
Lowering Knee Into Floor
If you want to keep tension on the muscle throughout the entire set, only lower the thigh down to where it is parallel to the floor or just slightly lower. If you are learning to activate the muscle or you are using a lot of resistance and need a break between reps, then you can lower down further, or all the way to the floor. The things to remember are that: the muscles will be working hardest when the leg is parallel with the floor; and the gluteus maximus is most active from neutral through extension (moving back behind the torso).

SCIENCY STUFF
SCIENCY STUFF
SPIFFILICIOUS FACTS ABOUT MUSCLES & MOVES
The gluteus maximus is a large muscle of the hip that originates on the back of the pelvic bones, the sacrum (the flat triangular bone at the end of the spine), the tailbone, and the fascia and ligaments. The gluteus maximus attaches to the femur (large long bone of the thigh) and the iliotibial band (IT band). When the muscle contracts it pulls the thigh back behind the body. This movement is relatively small - only about 15 degrees for most people. The hip is a ball and socket joint. The “ball” is the head of the femur, and the “socket” is a shallow bowl-like depression in the pelvis called the acetabulum.
The hip joint is the second least stable, designed-to-move, joint in the body. It can flex (forward motion), extend (backward motion), abduct (lift out to the side away from the body), adduct (move in towards the midline of the body, rotate in and out, and can circumduct - meaning it can move in a circle - which is a combination of the other movements that is constantly changing.
ALLLL MUSCLES & WHEN
ALL MUSCLES WORKING & WHEN DURING THE Donkey Kick - bent leg
In the beginning position, the core stabilizers ( internal and external obliques, quadratus lumborum, psoas major, rectus abdominis, erector spinae, multifidi, transverse abdominis) hold the spine in a neutral position.
The arm and shoulder blade muscles (deltoids, biceps, triceps, teres major, muscles of the forearm, scapular muscles, rotator cuff muscles) and the muscles of the non-working leg (hamstrings, quads, hip abductors and adductors, internal and external rotators) work to hold the body still.
The hamstring will hold the knee bent to 90 degrees. In this position the hamstring muscle is somewhat shortened, decreasing its ability to help extend the hip. The gluteus maximus is the prime mover that works to raise the leg up. Other muscles that may assist in extending the hip: are the gluteus medius and adductor magnus.
As the leg is lifted up all of the core muscles (internal and external obliques, quadratus lumborum, psoas major, rectus abdominis, erector spinae, multifidi, transverse abdominis), and the muscles of the arms and non-working leg (especially the gluteus medius and minimus) will contribute isometrically to stabilize the torso in the neutral spine quadruped (all fours) position.
The hip extensors will work eccentrically to control the movement of the leg as it is lowered back down.
PIN IT FOR LATER!