Dumbbell bus drivers exercise
How to Do the Dumbbell Bus Drivers Exercise (Front Delt) | In-Depth Guide [VISUAL LEARNERS]
Proper Form, Common Mistakes, & Variations | Home Resistance Training
WHAT DO YOU WANT TO SEE?
QUICK DEMO
QUICK DEMO
MUSCLES THIS WORKS
MUSCLES
MAIN MUSCLES WORKED IN the Dumbbell Bus Drivers Exercise
rotator cuff muscles
This exercises all 4 Rotator Cuff Muscles: the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis
OTHER MUSCLES WORKED:
- Scapular Muscles: Trapezius, Levator Scapulae, Rhomboids, Pectorals, Serratus Anterior, Latissimus Dorsi
WHAT WE'RE DOING TODAY
WHAT & WHY
BENEFITS OF TRAINING our rotator cuff muscles
WHAT
WHAT WE'RE DOING TODAY
ALL WE'RE DOING:
-Pretend you're turning the wheel of your car back and forth, except with a dumbbell-
TRAIN STABILITY & MOBILITY OF SHOULDER JOINT
These rotator cuff exercises train the smaller muscles of the shoulder joint to move the arm with control through a variety of rotational motions. In these exercises, the rotator cuff, and muscles of the shoulder blade and arm will be working together in coordination. Rotator cuff exercises are designed to train the muscles for both stability and mobility of the shoulder joint.
GREAT FOR BOTH WARMUP OR STAND-ALONE EXERCISES
The rotator cuff exercises can be used as a
- warm-up before upper body weight training
- as stand-alone exercises,
- in between arm strength training to increase blood flow and get the joints moving,
- or as a way to end a workout - giving the muscles just a bit more of a challenge and loosening up the joints.
Rotator cuff muscles are small muscles that need to be able to work at a low level for a long period of time. Think about how much you move your arms. Every time you move them all of the rotator cuff muscles need to work to help control the movement. This is important to think about when you are training the muscles.
USE LESS WEIGHT/RESISTANCE & MORE REPS
The rotator cuff exercises are done with lighter resistance and more repetitions - training the muscles to work at a lower level for a longer period of time. These exercises can be done daily. They are good exercises for when you take a break from sitting and working on a computer or after a long drive.
WHY BOTHER DOING IT?
WHY
WHY DO WE EVEN CARE?
ROTATOR CUFF EXERCISES ARE ALL ABOUT KEEPING HEALTHY SHOULDERS
The primary reason we have arms is to move the hand to different positions so you can use your hand. This means that the arm has to be able to move a lot and once the hand is where you want it to be, the arm is held still. The four rotator cuff muscles that surround the shoulder joint play a big role in making sure the way that the arm bone and shoulder blade are connected stay in healthy positions while we move the arm to prevent injury and long term damage to the joint. Strengthening these muscles with exercises like this one helps keep the shoulder joint healthy.
HOW ROTATOR CUFF EXERCISES CAN REALLY HELP US 40's AND UP LADIES SPECIFICALLY:
Much of the damage done to our bodies is when we are in our 20-30s, small amounts of damage over the years add up - examples are poor posture, working out with poor form, repetitive job tasks - repetitive lifting, too much sitting (desk jobs), especially when the chair, desk, computer set-up is incorrect and previous injuries - car accidents, falls, sports injuries. The body has an amazing way of compensating by using other muscles, or moving in different ways to accommodate for tight, weak or painful joints and muscles. Many times we are completely unaware of this, but eventually, it catches up.
Wear and tear over time, with the development of compensatory movement is the most common case for people to be in physical therapy, and mostly in people between the ages of 40 and 60. Fortunately, that is an age group that can still make a great difference in their physical abilities if they know what to do and what not to do.
Damage and weakness of the rotator cuff muscles can be caused by normal daily activities such as using a computer, texting, driving, reading, eating, cleaning, all involve using our arms in front of us, frequently with our shoulders rounded forward, slouched posture, and forward head. This position tightens the pectoralis muscles, and pulls the shoulders forward and into internal rotation, decreasing the space where one of the rotator cuff muscles travel through. Over time the joints of the upper back and ribs will become stiffer and the muscles of the back will weaken due to disuse. In the beginning you may not feel any restrictions, pain, or be aware of any weakness. If you continue down this path and don’t correct your posture, strengthen, and stretch, the joints will become even more restricted and the muscles weaker. The body has an amazing ability to compensate without awareness. You may begin to stand on your tiptoes to reach objects without realizing that your shoulder motion is limited.
As we age we do lose the elasticity of the soft tissues - the tendons and ligaments become stiffer. This makes them more prone to tearing (imagine a new rubber band that can easily be stretched, compared with an older one that may crack because it is not as stretchy). The production of the fluid in the joints can decrease (although it increases with movement). This reinforces the importance of taking time to warm up properly before exercise.
Additionally, disease processes can affect the rotator cuff muscles: for example, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, hypothyroidism all can affect the health of the tissues.
Stretching, strengthening, and correcting posture and movement can improve the health of the rotator cuff muscles and prevent future injury. With age you will lose muscle mass, beginning at 40. Exercise can prevent or reverse muscle loss - it is possible to gain strength even at 90 years of age. Bone density can decrease (with disease - osteoporosis/osteopenia) which can be slowed/reversed with exercise.
IDEAS FOR WHEN TO DO THESE MOVEMENTS:
PART OF DYNAMIC WARMUP: These are great to do as a part of a dynamic warm-up prior to working out. Warm-up movements increase blood and lymph (part of the immune system) flow, warms the connective tissue (muscle, tendons, ligaments, fascia) to improve their elasticity (will stretch instead of tearing), “wakes up” the muscles that will be worked - brings awareness to the muscles to improve the mind-body connection by actively contracting the muscles.
ON A REST DAY: Muscles get stronger by working them to the point of fatigue, this results in tiny tearing, called microtrauma of the tissue. The message sent to the brain is that the muscles are not strong enough to do the job that the body is trying to do. The response from the brain is to strengthen the muscle in order to improve its capability. Rest days are needed to allow the tissues to heal and grow. Part of the healing process is to remove the wastes and send in nutrients. Gentle movement will accomplish this.
END OF WORKOUT: If your goal is to improve the strength of the muscle it is important to fatigue the muscle. Adding these exercises to the end of a workout is a nice way of making sure that you have included some exercises that specifically address the rotator cuff muscles, in addition to making sure that you have properly fatigued the muscle.
WHEN SHOULDERS ARE FEELING “STICKY” DURING WORKOUT: Motion is Lotion - moving improves the mobility of the joints and soft tissues. “Sticky” areas in movements can be caused by a number of things - poor joint mobility which can be caused by insufficient joint lubrication (synovial fluid), stiff ligaments, or tightness or stiffness of the muscles, tendons, or fascia. Movement can help in all of these cases: increases the synovial fluid in the joints, increases the temperature and therefore the elasticity of the muscles, tendons, and fascia by increasing blood flow.
Fascia is a thin sheet of connective tissue running throughout the body between the muscle and the skin. The fascia allows the skin to be able to glide effortlessly over the muscle (you can feel this by taking your fingers and gently moving the skin over the underlying muscles. Sometimes you get restrictions in the fascia where it no longer glides smoothly with movement (frequently happens around scars). Tendons run in sheaths of connective tissue and are surrounded by a layer of fluid, sometimes the tendon can get hung up somewhere in the sheath and feel caught or stuck, movement can help to loosen this restriction. By warming up with larger, fluid, movements that combine many directions of motion you “floss” the tendons in the sheath and improve the ability to glide these soft tissues. Leading to freer, unrestricted movement.
HOW FREQUENTLY CAN THESE EXERCISES BE DONE?
Exercises that work the endurance muscles can be done daily. This includes core exercises, balance and stability training. The muscles work at a low level for a long period of time every day. The reason for giving a rest to the larger power muscles is that in order to strengthen those muscles you need to use heavy weights and push them to the point of failure - actually causing small tears in the tissue. The muscle needs a day to make the repairs to the tissues. The endurance muscles are worked at a low level for an extended period of time, the training is more focused on form and muscle re-education as opposed to muscle failure.
EVERYDAY LIFE
EVERYDAY LIFE &
MUSCLE FUNCTION
HOW WE USE OUR ROTATOR CUFF MUSCLES IN EVERYDAY LIFE
1. SUPRASPINATUS [LIES ABOVE THE SPINE OF THE SCAPULA]
- Lifting and holding the arm out to the side (shoulder abduction)
- Pulling up pants
- Lifting and carrying a car seat at your side.
- Holding the arm in the socket against a downward pull on the arm (assisted by the deltoid)
- Lifting and carrying heavy items
2. INFRASPINATUS [LIES BELOW THE SPINE OF THE SCAPULA] AND TERES MINOR
- Rotates the upper arm outward - the soft underside turns outward (external rotation)
-
- Outstretched arm
- Turning the arm over to receive change
- Turning arms outward to carry a large tray or getting a roasting pan out of the oven
3. SUBSCAPULARIS [LIES ON THE UNDERSIDE OF THE SHOULDER BLADE - THE SIDE BY THE RIBCAGE]
- Rotates the upper arm inwards (internal rotation)
- Keeping the forearm still while pouring out a jug of water
STARTING POINTERS
Starting Pointers
Bus Drivers work all four of the rotator cuff muscles and the deltoid muscle.
The movement is pretty much just as you would imagine it would be. The arms move as if they were turning the steering wheel of a bus.
The rotator cuff muscles work to control the movement of the upper arm bone during the rotational motion. The upper arm will rotate from internal to external rotation. The exercise will also work the muscles of the hands and arms. The muscles are working constantly - just to hold the weight up. And, since the movement is constant and the direction of the movement is changing, the muscles need to continue to change how they are working. This is a very effective way to train the rotator cuff how to respond to the movement and keep the joint stable.
HOW TO FEEL WHAT MUSCLE IS WORKING
How to Feel What Muscle is Working
These are small, deep muscles that cross the shoulder joint. The best way to feel them working is to try to relax the larger muscles of the arm. Bend the elbow to 90 degrees and slowly the upper arm bone in and out - your forearm and hand moving in an arc-like a windshield wiper. You may not be able to feel the muscles working but you should be able to feel the upper arm bone rotating.
HOW TO DO THE EXERCISE
LOOKS
HOW Dumbbell Bus Drivers Exercise SHAPE OUR BODY
This exercise improves upright posture, decreases rounded shoulder posture.
Tones the shoulders and arms. The supraspinatus and infraspinatus can provide shape to your upper back and upper shoulder (under the upper trap).
PROPER FORM
PROPER FORM: Dumbbell Bus Drivers Exercise
EQUIPMENT, SETS & REPS
EQUIPMENT
SUGGESTED STARTING WEIGHT FOR WOMEN:
5-8 pounds (1)
SETS & REPS:
1 set of 10-15 or to fatigue; Optionally - time the exercise for 20-30 seconds, you can do one or two sets.
PACE:
Smooth controlled pace. Slower will be harder.
BODY POSITION
BODY POSITION FOR THE Dumbbell Bus Driver Exercise
FEET: Shoulder width apart, toes straight ahead.
BODY STANCE: Knees slightly bent to create a stable base to work off of. Neutral spine; Shoulder blades pulled down your back. Sternum lifted. Abdominals gently engaged.
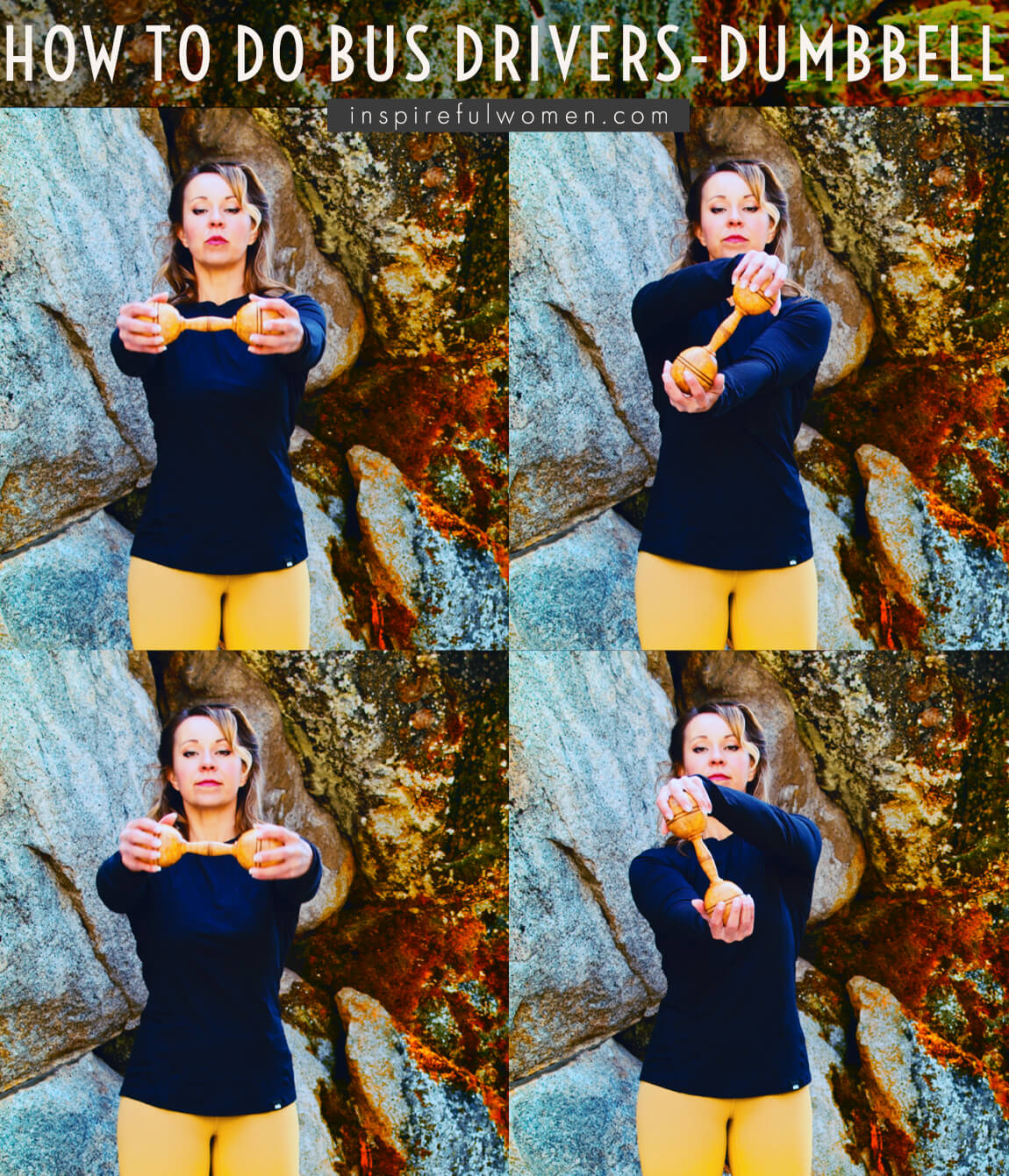
HAND/GRIP: One hand gripping each end of the dumbbell - spread fingers out to firmly encase the ends, Dumbbell is horizontal to start.
ARM: Arms are held parallel to the floor. When the weight is turned so that the handle is vertical, the top hand should be at shoulder height. Elbows should have a slight bend.
NECK: Relaxed and neutral, not involved in the movement.
HOW TO DO
HOW TO DO Dumbbell Bus Drivers Exercise
CUE: To get the most out of this exercise, focus on the pattern, following a true circle, without cutting corners. This will increase the activity of the rotator cuff muscles.
Slowly rotate the weight clockwise as far as you are able to as if you were making a right turn. The bottom hand will be at the end range at approximately 7 - 8 o’clock.
Without pausing, rotate counterclockwise (left turn) back to the start position.
Repeat for the desired number of reps.
HOW TO SAFELY GET OUT OF THE EXERCISE
Squat down and set the weight on the floor.

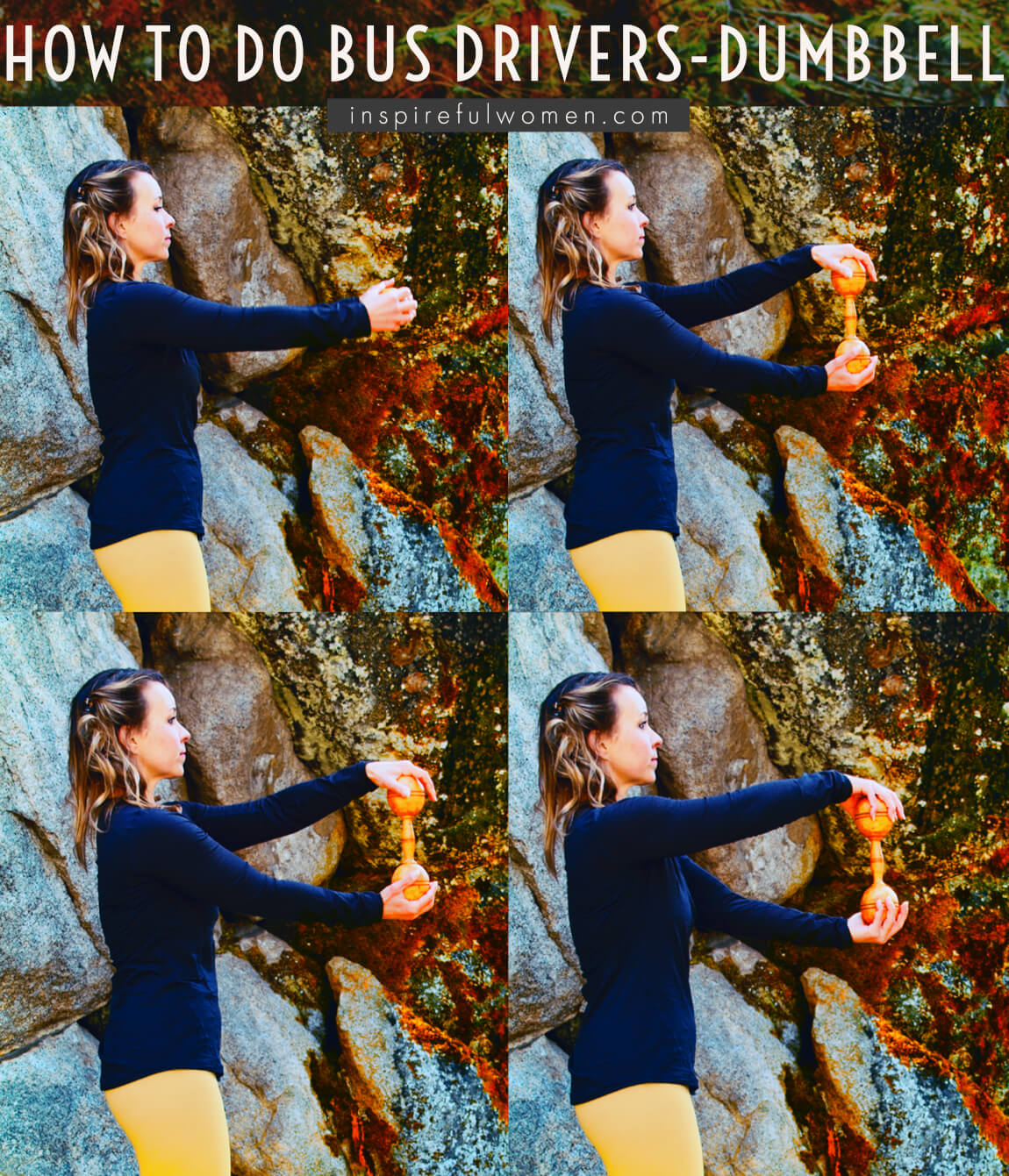
COMMON MISTAKES
COMMON MISTAKES
WHAT TO AVOID WITH THE Dumbbell Bus Driver exercise
KEY TIP:
Guess what? Good news! Many avoids are the same for most movements. Once you learn the basics, there's really only a few extra avoids for each individual movement.
1. Avoid tightening the neck muscles
AVOID: Avoid tightening the neck muscles
WHY NOT?
- Will interfere with the proper movement of the shoulder joint
- This can lead to neck or shoulder strain, injury, or damage over time.
- You may feel neck discomfort, find that you are pressing down with your head, or gripping with your neck muscles.
- This will defeat the purpose of the exercise, the goal is to move the upper arm using the small muscles.

2. avoid using only wrists
AVOID: Avoid using only the wrists
WHY NOT?
- Moving the wrist instead of the upper arm will not work the rotator cuff muscles.
- Poor alignment (bent forward or backward) or repetitive movement through the wrist can lead to joint and/or soft tissue irritation or injury over time.
WHAT TO DO:
- Your wrists should be in line with your forearm and should be still throughout the exercise.

3. Avoid shoulders hunching Up
AVOID: Avoid moving your shoulders up and down as the arm moves.
WHY NOT?
- Will interfere with the proper movement of the shoulder joint which can result in soft tissue or joint irritation, injury, or damage over time.
- Moving the shoulder up and down will not work the rotator cuff muscles.
WHAT TO DO:
- The shoulder blade may rotate up or down but avoid lifting the shoulders up.
- Maintain good posture with the sternum lifted, space between your earlobe and the top of the shoulder.

4. Avoid cutting off the circle
AVOID: Avoid cutting off the circle - soft elbows as you go around
WHY NOT?
- This will decrease the muscle activity of the rotator cuff muscles
WHAT TO DO:
- The goal of this exercise is to retrain the rotator cuff muscles for controlled and small precise movements, focus on controlling the movement by making a rounded 8

VARIATIONS
VARIATIONS
VARIATIONS OF Dumbbell Bus Drivers
ball Bus Driver
Ball Bus Driver
STABILITY BALL: Hold the ball in your hands instead of a dumbbell to work the muscles through a larger range of movement. One hand on top and the other hand on the bottom.
SPORTS BALL: Use a ball that has some weight - basketball, soccer ball, volleyball. One hand on top and the other hand on the bottom.
WEIGHTED BALL: Use a weighted exercise ball. The ball should be 10 inches in diameter or larger. One hand on top and the other hand on the bottom.

SCIENCY STUFF
SCIENCY STUFF
SPIFFILICIOUS FACTS ABOUT MUSCLES & MOVES
SHOULDER IS MOST MOBILE JOINT IN BODY - UPSIDES & DOWNSIDES TO THAT
The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint - meaning that one part of the joint is shaped like a ball and the other side of the joint is like a socket. The “ball” is the end of the upper arm bone (head of the humerus) and the “socket” is a small shallow cup on the shoulder blade (glenoid fossa of the scapula). The joint is the most mobile joint and the least stable joint in the body. This allows large movements of the arm. That is the upside to such a mobile joint.
The four rotator cuff muscles; the infraspinatus, supraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis; lie on the shoulder blade and attach to the upper arm bone. They form a cuff around the joint to provide support and stabilize the arm during movement. All of the muscles work together to help keep the “ball” in the “socket”. This is commonly described as like trying to keep a golf ball balanced on the tee - that is approximately the size difference between the ball of the upper arm bone and the socket of the shoulder blade. When you move your arm, the rotator cuff muscles must keep the ball centered on the tee. This is complicated by the fact that the ball needs to move around in the socket as the arm moves.
A downside to such a mobile joint is that it can be more easily injured. Exercises to train and maintain the health of the four rotator cuff muscles protects the shoulder joint from injury and/or long term gradual damage.
PICTURE THE SHOULDER JOINT
Make a fist with 1 hand - that’s the ball head of the upper arm bone
SLIGHTLY cup the other palm - that’s the small cavity on the shoulder blade that the ball sits against/into. The rotator cuff muscles keep the ball pulled against this concave surface.
TRAINS THE MUSCLES THAT KEEP THE PARTS OF YOUR SHOULDER JOINT IN THE RIGHT PLACE WHILE YOU MOVE
The job of the rotator cuff muscles is to make sure the two main shoulder joint surfaces (ball and socket) are positioned correctly* so that the movement does not damage the labrum (soft cartilage), ligaments, or tendons as the arm moves. This is even more important when you are lifting, pulling, pushing, carrying any weight. When you are exercising it is a good idea to warm up/or “wake up” these muscles before upper bodyweight training.
* poor shoulder joint mechanics (this means that the joints and muscles that move the shoulder blade, collarbone and arm are not working together) can result in damage to the soft tissues that support the joint (tendonitis, tendonosis, muscle/tendon tears, glenoid labrum tears). This joint “sloppiness” (too much uncontrolled movement in the joint) can cause osteoarthritis (degenerative changes in the joint) - spurring and erosion of the bone surfaces.
NEGLECTING THESE MUSCLES CREATES IMBALANCE SETTING US UP FOR INJURY
It is important to include exercises for the rotator cuff muscles in your upper body training. The rotator cuff muscles are the support muscles, they need to be healthy and well trained in order for you to be able to lift heavy items.
If you neglect the rotator cuff muscles and only train the large muscles that move the arms you will be creating imbalances in the muscles - the big muscles can lift a lot of weight but the supporting muscles cannot. This sets the shoulder up for injury. To visualize this think of using a small slender and flexible fishing rod and catching a heavy fish. When you try to pull the fish in, the rod would just bend, and could possibly break. If the rod is more stable and stiffer you will be able to pull in the larger fish.
ALLLL MUSCLES & WHEN
ALL MUSCLES WORKING & WHEN DURING THE Dumbbell Bus Driver Exercise
The deltoids work throughout this exercise to hold the arms up. As the weight is rotated the different parts of the deltoid are targeted. When the hand is at the top of the weight, the shoulder will be flexed and internally rotated (anterior deltoid, biceps, coracobrachialis, subscapularis, pectoralis major) As the dumbbell is rotated downward the medial deltoid will become more active. At the bottom of the movement, the anterior deltoid will be most active, along with the external rotators (infraspinatus, teres minor).
The deltoids, biceps, triceps, latissimus dorsi, pectoralis, will all be under constant tension to hold the weight of the dumbbell in front of the body at shoulder height. The four rotator cuff muscles will be working throughout the exercise to keep the head of the humerus centered in the socket of the shoulder joint. The rotational movement works the rotator cuff muscles. As the weight is rotated the contribution from the different muscles changes. The muscles of the back will be working to rotate the shoulder blades and the weight is rotated, and to stabilize the spine.
PIN IT FOR LATER!










