Lateral Step Ups
How to Do the Squat Alternative: Side Step Downs at Home | In-Depth Guide [VISUAL LEARNERS] Beginner
Proper Form, Common Mistakes, & Variations | Home Resistance Training
WHAT DO YOU WANT TO SEE?
QUICK DEMO
QUICK DEMO
MUSCLES THIS WORKS
MUSCLES
MAIN MUSCLES WORKED IN Lateral Step Ups
Quadriceps & Gluteus maximus
OTHER MUSCLES WORKED:
- Hamstrings
- Gastroc & Soleus
- Gluteus medius & minimis
STARTING POINTERS
Starting Pointers
WHAT WE'RE DOING TODAY
Other names for this exercise: Lateral Box Step Ups, Side Step Downs
Lateral Step Downs still work the large muscles of the thighs, but they will also work the muscles on the side of the hip more. The gluteus medius and minimis are the muscles on the side of the hip that move the thigh out to the side - called hip abduction. The exercise is done with the body standing sideways on the top of the step. The non-working leg is held off the step to the side. The muscles of the side of the hip on the working side need to contract to keep the pelvis from tilting down. It is important to focus on keeping your pelvis level as you bend the ankle, knee, and hip of the working leg.
Healthy hip abductors are needed for normal walking – when all of the weight is on one leg the hip abductors of the weight-bearing leg must contract to hold the thigh upright and prevent the pelvis from tipping. These muscles help align the leg to prevent the knee from falling inward (knock knees) and the foot from pronating (arch collapsing inward). Poor alignment of the knee and foot contributes to many problems with the leg, including knee and hip pain, wear and tear on the ankle, knee, and hip joints, plantar fasciitis, bunions, and even pelvis and low back joint pain.
It is tempting to think about lowering the non-working foot to the floor instead of thinking about bending the ankle, knee, and hip of the working leg. Although it seems like a small thing it makes a big difference. When you give your brain the task of lowering the non-working foot to the floor, it will want to do it the easiest way possible, which is to let gravity pull that side of the hip down.
HOW TO DO THE EXERCISE
LOOKS
HOW Lateral Step Ups SHAPE OUR BODY
Toned buttocks, and thighs (front and back). Works the muscles needed for healthy upright posture.
PROPER FORM
PROPER FORM: Lateral Step Ups
EQUIPMENT, SETS & REPS
EQUIPMENT
Step-Up
Small one with several heights for space saving:
Goes from 2-12" high & you can buy extra risers for it (I did) - they are the standard riser used with all the other regular step-ups that are a longer length, so any will do.
Extra risers - set of 2 will give you 4" extra for 16" height total.
The the only thing you might have a little trouble with with this one is doing a hip thrust on it (where you're back is on the step) - but it CAN work.
Start at 8 inches and increase as form improves.
SUGGESTED STARTING WEIGHT FOR WOMEN:
Bodyweight
SETS & REPS:
2 sets of 8 reps
PACE:
Slow and controlled throughout.
BODY POSITION
BODY POSITION FOR THE Lateral Step Up
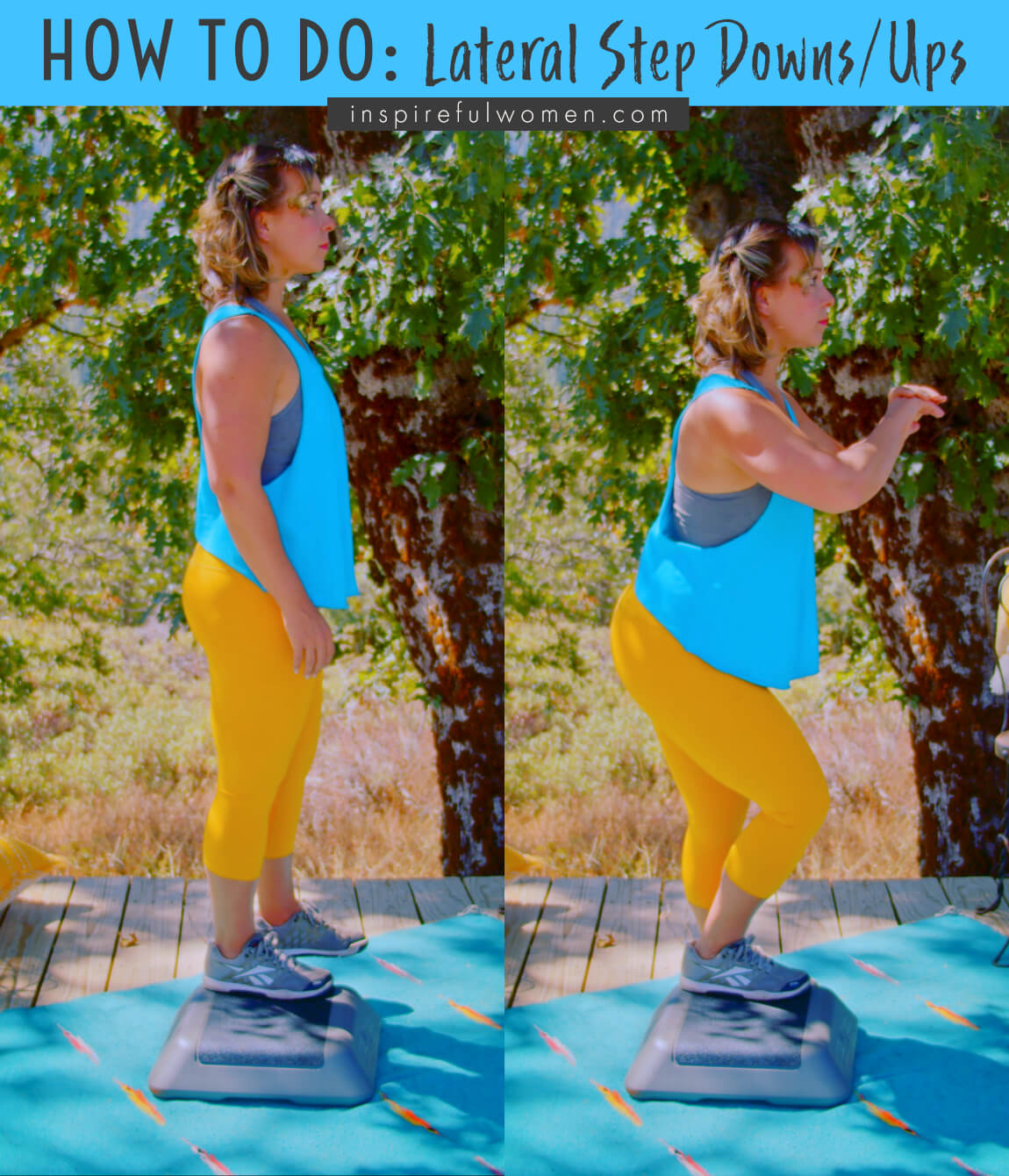
FEET: Stand on the step and turn sideways with your feet a few inches apart. Move over towards the edge of the step so that your foot closest to the edge is barely on the step. Your feet are flat with your toes pointed forward. Your working leg will be the leg that is on the inside.
BODY STANCE: Neutral spine. Hips and shoulders are level and square.
ARM: Relaxed by your side.
HOW TO DO
HOW TO DO Lateral Step Ups
CUE: The most important part of the exercise is controlling your pelvis and keeping your knee stable and tracking right over your foot.
Move your leg that is closest to the side of the step off of the step so that you are holding it above the floor at the height of the step. Your legs should be about hip-width apart with your non-working leg suspended above the floor. Make sure that your pelvis is level.
Your shoulders should be lined up over your hips which are over the foot of your working leg (the foot on the step).
Keep your pelvis level and square to the front as you slowly bend at your ankle, knee, and hip to lower yourself down. When you bend at your hips (hip hinge), your bottom will move backward (very slightly) but your shoulders will stay over your foot. Your knee will travel over your toes. Keep your heel down.
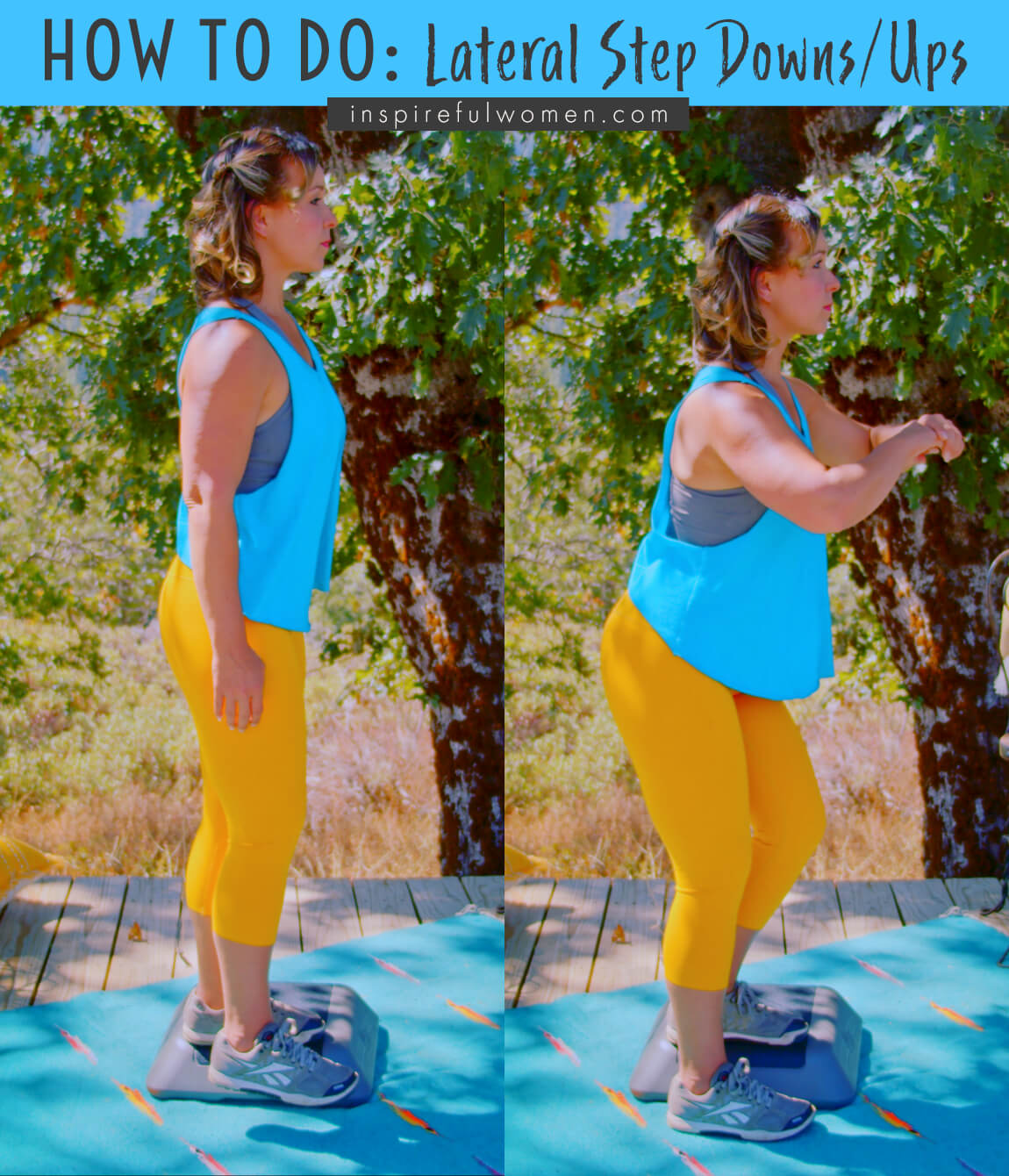
When you get to the bottom of the movement, lightly tap your heel to the floor – do not transfer your weight to your non-working leg.
To return to the start position, push down into the step and straighten up at your ankle, knee, and hip. Make sure that your knee and hip are fully extended at the top of the movement.
Keep your non-working leg held out to the side and continue with the next rep.
HOW TO GET OUT OF THE MOVEMENT: Step down off of the step.
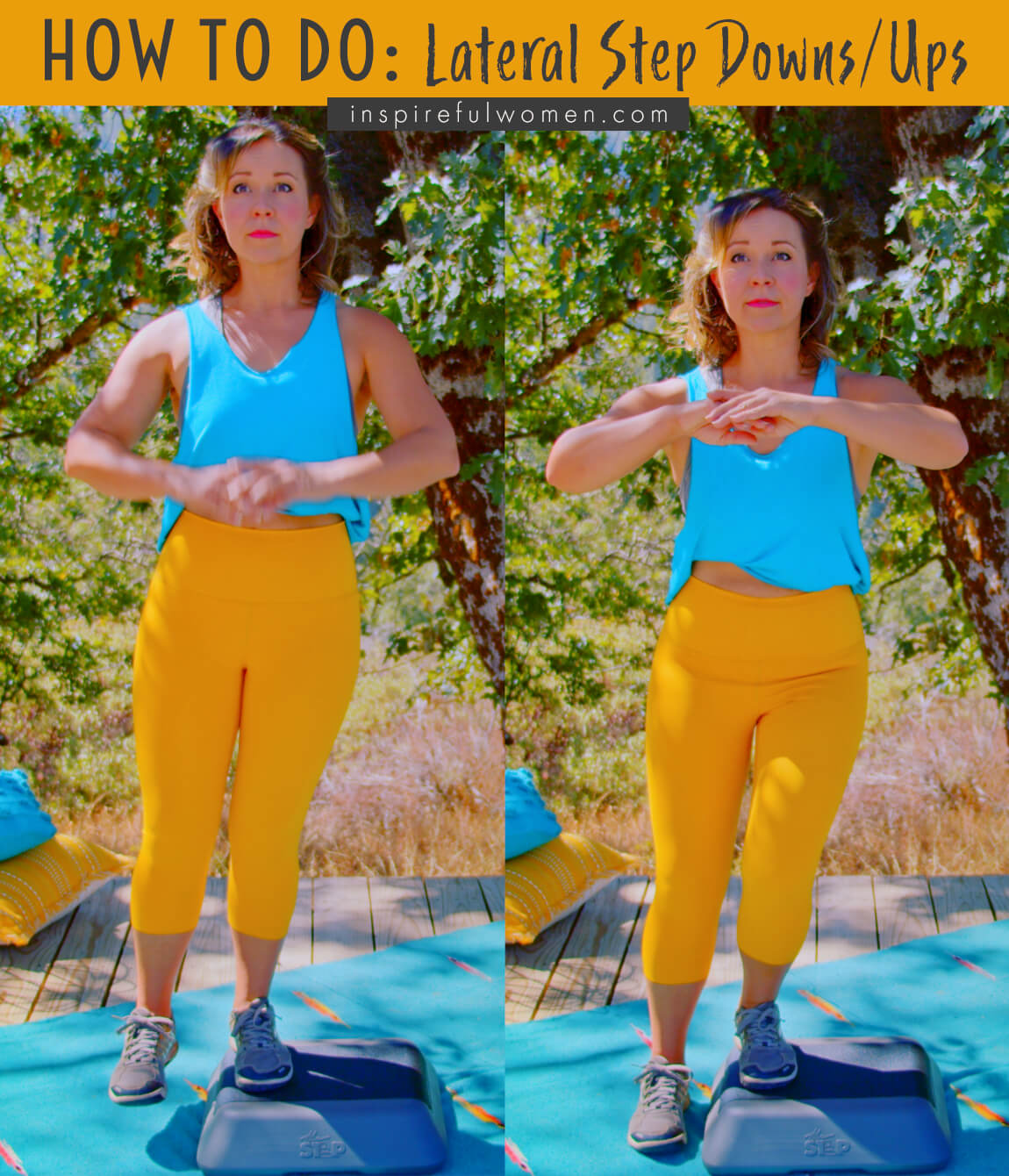


COMMON MISTAKES
COMMON MISTAKES
WHAT TO AVOID WITH THE Lateral Step Up
KEY TIP:
Guess what? Good news! Many avoids are the same for most movements. Once you learn the basics, there's really only a few extra avoids for each individual movement.
1. Avoid Hip Dropping
AVOID: Dropping the hip on the side of the non-working leg.
WHY NOT?
- Dropping the non-working side of the pelvis is a common mistake.
- It results in moving less through the hip and knee and more in the back.
WHAT TO DO:
- Your pelvis should be level throughout the exercise.
- Watching your form in a mirror can help.

2. Avoid Letting the Toes Drop
AVOID: Letting the toes drop down or point to the floor.
WHY NOT?
- It will reduce the range of motion our leg is working through.
WHAT TO DO:
- Limit the movement of the foot – try not to supinate or pronate.

3. Avoid Stretching Wobbling of Non Working Leg
AVOID: Uncontrolled movement of the leg.
WHAT TO DO:
- The knee should be in line with the 2nd and 3rd toes throughout the exercise.
- Keep the foot in good alignment to
Promote better alignment of the entire leg
Train the muscles to hold the foot in good alignment to prevent injury
Strengthen the muscles of the foot for improved balance and stability.
4. Avoid Stretching Foot To Floor
AVOID: Stretch your leg down to touch to floor.
WHY NOT?
- This will result in your hips dropping.
5. Avoid Dropping Down
AVOID: Avoid “dropping” back down to the floor.
WHY NOT?
- Stepping down is equally as important as the stepping up part of the exercise.
WHY NOT?
- Stepping down is equally as important as the stepping up part of the exercise.
VARIATIONS
VARIATIONS
VARIATIONS OF Lateral step ups
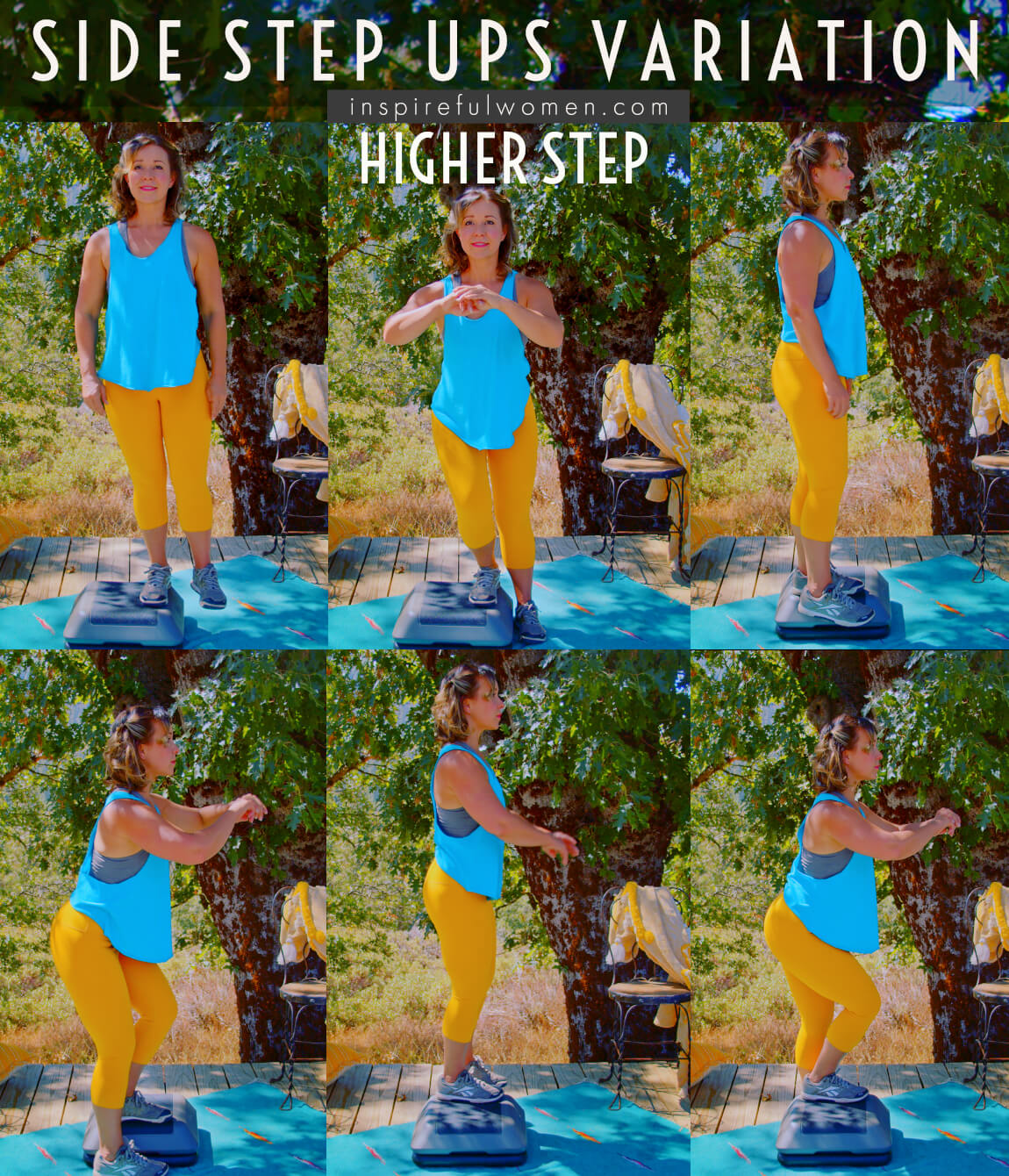
HIGHER STEP
Higher Step
Choose a step height that you are able to use with the correct form but is challenging.

WHAT WE'RE DOING TODAY
WHAT & WHY
BENEFITS OF TRAINING THE glutes & Quadriceps
WHAT
STEP UPS OR STEP DOWNS?
First, let’s talk about the naming of these movements. In step ups and downs the muscles are working as you step up AND as you step down. You will find that the names of the movements vary quite a bit. What one person refers to as a forward step up may also be called a reverse step down, etc. This can be confusing but, the naming is just opinion, most likely based on what the focus of the exercise should be - the up phase of the down phase. For the purpose of our naming, there are a few ways to sort through this.
If you are behind the step, facing the step as you would walk upstairs, it makes sense to call that a “step up” position. If you are in front of the step or on the step facing away from the step, as if you were walking downstairs, it makes sense to call that a “step down” position.
If you start on the floor and step up onto the step first and then step off of the step, that could be thought of as a step up. And, likewise, if you start on the step and begin the set by stepping down to the floor, that could be a step down exercise. That helps to clarify the movement when you are facing toward or away from the step. When you are standing sideways on the side we will just call that one “Lateral Step Downs” because you begin the movement from the top of the step.
Like most exercises, this movement works the same muscles throughout the entire movement, both as you are stepping up and as you are stepping down. The muscles are worked in two different ways. For example, during a forward step up, the targeted muscles shorten (concentric contraction) to extend the leg and lift the body up onto the step. The same muscles contract as the muscle is lengthening (eccentric contraction) and the body is lowered back down to the floor. It is fairly common to forget this when you are doing step ups, and let gravity just pull down back down to the floor. Lower yourself back down slowly and with control.
Step ups and step downs are a group of exercises that work the knee extensors and the hip extensors together. The knee extensors are the quadriceps muscles on the front of the thigh. The main function of these muscles is to straighten the knee. The main hip extensors work to straighten the hip, they are the gluteus maximus and the hamstrings. In these exercises, you will be stepping up or down off of a box or step. Different versions of the exercise will face different directions - towards the step, away from the step, or sideways. Even though the same muscles will be working in all of the exercises, it is surprising how just changing the direction of the stepping feels very different.
Step ups and downs will help to strengthen the leg muscles. But, the main focus of these exercises is learning good form - motor control, balance, and stability. It is pretty easy to make these exercises easier or harder. But first, it is important to make sure your form is correct. Although we are very used to going up and down stairs, it is fairly common to use gravity and momentum to help you. Learning the correct form helps to train the muscles of the core to hold your torso still as you use the leg to move your body. Going up and down stairs the correct way will strengthen the leg muscles and prevent straining the back, not just in exercise, but in daily life. Try to resist the urge to use a taller step and sacrifice good form.
Pay close attention to the alignment of your foot, ankle, knee, hip, and pelvis during these exercises. Even the muscles of the feet will be working. Try to keep the leg as still as possible (not wobbly). It is tempting to think about lowering the non-working foot to the floor instead of thinking about bending the ankle, knee, and hip of the working leg. Although it seems like a small thing it makes a big difference. When you give your brain the task of lowering the non-working foot to the floor, it will want to do it the easiest way possible, which is to let gravity pull that side of the hip down. It is not necessary to tap the non-working foot on the floor. Avoid lowering down past the point of being able to maintain good form. The goal is to go as low as you can while maintaining good form.
WHY BOTHER DOING IT?
WHY
WHY DO WE EVEN CARE?
TRAINING EVERY DAY LIFE STRENGTH
There are many good reasons for including step ups and downs in your exercise program. These exercises train you to use your body the way it was designed to be used. The goal of the exercise is to hold the torso in a neutral position and still as you use your leg to move your body up and down. This is exactly how we should be moving in many daily activities. Working on keeping the legs and spine in good alignment, while moving through the ankles, knees, and hips will strengthen the muscles of the torso and the legs with the least amount of stress on all of the joints.
SINGLE LEG EXERCISES GREAT FOR BALANCE & STABILITY
This movement is done one leg at a time. Single leg exercises have the added benefit of training balance and stability. All of the muscles in the foot, and those that cross the ankle, knee, and hip will have to work together to keep the lower limb aligned and stable. Good alignment of the lower limb reduces the stresses on the joints to help to prevent age-related changes. Common age-related changes include muscle imbalances, joint surface wear and tear (osteoarthritis), decreases in range of motion, and increased risk for falls.
Single-leg exercises can help make you more aware of any left and right differences in the range of motion of the joints, leg strength, or ability to balance. If you find that you are more limited on one side, work on that side a little bit more to try to correct the differences. Keep in mind that in single leg exercises, the working leg is moving 100% of your body weight.
EVERYDAY LIFE
EVERYDAY LIFE &
MUSCLE FUNCTION
HOW WE USE OUR Quadriceps and Gluteus maximus IN EVERYDAY LIFE
THE QUADRICEPS STRAIGHTENS THE KNEE AND THE GLUTEUS MAXIMUS STRAIGHTENS THE HIP DURING:
- Climbing upstairs
- Climbing a ladder
- Walking uphill
- Getting up from a squat
- Pushing up from the floor
- Rising from the toilet or chair
- Stepping into a high vehicle
THE QUADRICEPS HELPS TO CONTROL THE BENDING OF THE KNEE AND THE GLUTEUS MAXIMUS HELPS TO CONTROL THE BENDING OF THE HIP DURING:
- Going down stairs
- Going down a ladder
- Walking downhill
- Lowering down into a squat
- Getting down to the floor
- Lowering down to the toilet or chair
- Climbing out of a high vehicle.
SCIENCY STUFF
SCIENCY STUFF
SPIFFILICIOUS FACTS ABOUT MUSCLES & MOVES
The musculoskeletal system is the body’s system that is responsible for movement. The parts of the system work together as a whole. The brain programs the movement patterns and along with the nerves, orchestrates out all voluntary movement. When the parts of the system (joints, muscles, nerves, soft tissues) are healthy, each part does its job. The movement will put the least amount of stress on all parts of the system and will use the least amount of energy to achieve its task. But, even small amounts of weakness, pain, instability, or lack of motion can affect the entire system. For example, restricted ankle movement will affect the movement at the knee, hip, pelvis, and spine. The brain must reorganize the movement pattern to adjust for the deficit. This is known as compensatory movement patterns.
Compensatory movement patterns can lead to new problems in other parts of the system. When you ask your body to work in a way that it was not designed to work, it usually cannot accomplish the task without causing increased stress and energy requirements. Step ups and downs work the entire lower body together. All parts need to do their job effectively in order to safely complete the movement. This exercise is frequently used as a way to identify and address areas of weakness. The focus of the exercise is on form and control. It is important to keep the entire lower limb, pelvis, and spine aligned during the movement. Mastering step-ups and downs will help to reinforce healthy movement patterns that are used in many daily activities.
ALLLL MUSCLES & WHEN
ALL MUSCLES WORKING & WHEN DURING THE SIDE Step Up
The gluteus medius and minimus must work throughout the movement to hold the pelvis level as the quadriceps, gluteus maximus, hamstring and calf (gastrocnemius and soleus) muscles are working throughout the exercise to control the movement of the hip, knee and ankle. The core stabilizers work throughout the movement.
The muscles work together to stabilize the leg as they contract eccentrically to decelerate the weight of the body as it is pulled down to the floor. The lateral step down begins with an eccentric contraction of the quadriceps as the knee bends, and the calf muscles as the ankle bends. The gluteus maximus and hamstrings will become active to control the hip flexion. To return to the start position the quadriceps and calf muscles contract concentrically to straighten the leg. The gluteus maximus and hamstrings straighten the hip as the body is pulled back up onto the step.
PIN IT FOR LATER!





